SWOT Analysis
SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis is a framework used to assess a company’s competitive standing and to develop a strategic plan. A SWOT analysis is designed to facilitate a discussion of the strengths and weaknesses of an organization. In doing so, the SWOT analysis assesses internal and external factors and current and future possibilities.
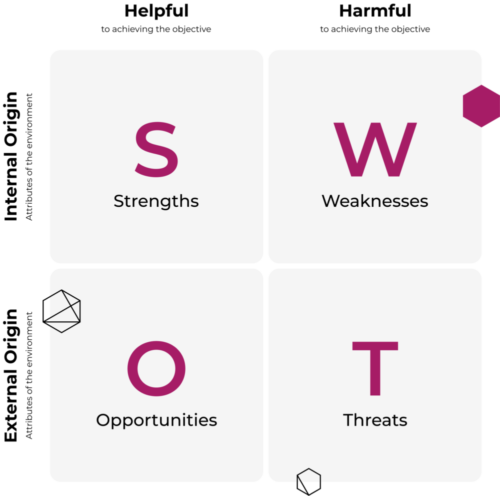

A SWOT analysis graph is a tool that can help you to analyze what your company does best today and to devise a successful strategy for the future. SWOT can also uncover business areas that is holding your company back, or that your competitors could exploit if you don’t protect yourself.
However, traditional SWOT exercises are done manually, often on a physical or digital whiteboard, and often in groups which can lead to certain types of bias. Fortunately, the advantages of Quantumrun’s version of SWOT includes:
- The ability for your team to source trend insights from the Quantumrun platform;
- Facilitating a blind vote for each SWOT topic in the project so that its graph position represents the team’s unbiased, collective perspective;
- Positioning each topic by its average year and likelihood scores as assigned by your team (e.g., instead of positioning a topic randomly inside a SWOT quadrant, as is common in whiteboard/paper exercises.)
How to Conduct a SWOT Analysis
Choose an organizational leader who can facilitate a discussion with multiple participants. You want an individual who will ensure that all participants are heard in the discussion.
Tip: If your organization is interested in an external facilitator, we can assist you.
Work with your team to identify the perceived strengths of your organization. Strengths describe what internal factors an organization excels at: a strong brand, loyal staff, a dedicated client base, balanced finances, unique technology, etc.
During your Strengths analysis, ask some of the following questions:
- What do we do well or best?
- What’s unique about our organization?
- What does our target audience like about our organization?
- In what ways do we excel past our competitors?
Work with your team to identify the perceived weaknesses of your organization. Weaknesses describe what internal factors prevent an organization from performing at its best. Weaknesses are areas for improvement to remain competitive, including a weak brand, higher-than-average turnover, high levels of debt, etc.
During your Weaknesses analysis, ask some of the following questions:
- Which initiatives are underperforming and why?
- What can be improved?
- How could improve our performance?
- What services or resources can assist?
- How do we rank against our competitors?
Work with your team to identify the perceived opportunities for your organization. Opportunities describe promising external factors that may give the organization a competitive edge. For example, an expanding online marketplace, international trade agreements, etc.
During your Opportunities analysis, ask some of the following questions:
- What resources can we use to improve weaknesses?
- Are there market gaps in our services and products?
- What do our competitors offer that we may not?
- What are our goals for the year?
Work with your team to identify the perceived threats to your organization. Threats describe external factors that may harm the organization—for example, the rising costs for materials, increasing competition, tight labor supply, etc.
During your Threats analysis, ask some of the following questions:
- What changes in the industry are concerning to us?
- What new market trends are seen in and outside of our sector?
- Where and how are our competitors outperforming us?
After identifying your SWOTs your team can begin to outline a strategic plan to tackle each sector of the analysis. This involves deciding which opportunities will be prioritized and creating action plans to address your organization’s weaknesses and competitive threats.
When would you use a SWOT instead of VUCA graph?
SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) is used for analyzing and understanding the internal and external factors that may impact an organization’s success.
VUCA (Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity, Ambiguity) is used to describe and understand the nature of the rapidly changing and unpredictable world.
SWOT is best used when the situation is relatively stable and well-defined, while VUCA is more relevant in situations where rapid change and unpredictability are present.



